Safe Work Australia
Safe Work Australia (SWA) is the Australian Government statutory body established to develop national policy relating to WHS and workers’ compensation.
SWA is jointly funded by the Commonwealth, State, and Territory Governments through an Intergovernmental Agreement. SWA is a tripartite body working in partnership with governments, employers, and employees. SWA works to:
- develop and evaluate national policy and strategies
- develop and evaluate the model WHS legislative framework
- undertake research, and
- collect, analyse, and report data.
Safety Authorities
Safety authorities operate within each Australian State and Territory as a governing body to ensure that employers meet their legislative requirements under the Occupational Health and Safety laws.
State and Territory authorities are:
- SafeWork NSW
- WorkSafe ACT
- WorkSafe Victoria
- SafeWork South Australia
- WorkSafe Western Australia
- NT WorkSafe – Northern Territory
- Workplace Health and Safety Queensland
- WorkSafe Tasmania
Comcare is the national authority for work health and safety, and workers’ compensation. They promote the health benefits of good work.
The Health and Safety Framework
To ensure that an organisation meets all the requirements for a healthy and safe workplace the Health and Safety Framework needs to be understood and applied within an organisation.
The Health and Safety Framework contains the following:
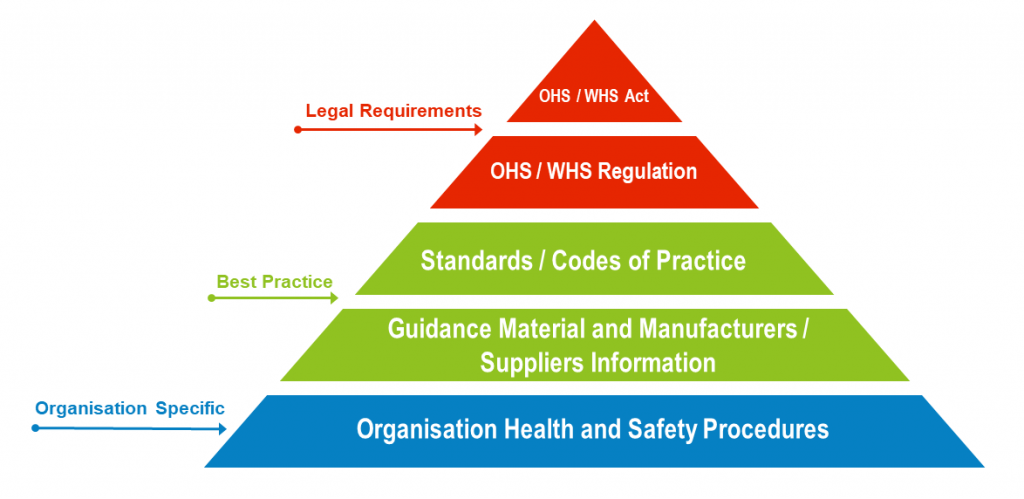
Health and Safety Legislation
State and Territory Government legislation, both Acts and Regulations covering occupational health and safety, or workplace health and safety are mandatory proactive pieces of legislation that aim to protect the health, safety, and welfare of workers by setting general requirements which must be met at places of work. The provisions of the legislation cover employers and employees in every place of work.
Occupational Health and Safety Acts establish broad principles of health and safety while the regulations contain the necessary detail to ensure that the principles of the Act will be achieved by employers’ compliance.
To maintain a safe and healthy work environment everyone in the workplace – frontline employees, supervisors and managers must work together to promote and support the principles of Health & Safety.
Under health and safety law employees have the right to:
- a safe and healthy workplace
- safe ways of working
- safety information
- health and safety training
- safety equipment
- be consulted on health and safety
- select health and safety consultation and communication arrangements
- leave their work area to report a health and safety problem
The law also outlines that both employers and employees have a responsibility for ensuring that health and safety guidelines are adhered to. These responsibilities are:
Employers’ Responsibilities
- provide a safe and healthy workplace for employees and people visiting their places of work who are not employees (customers, contractors, visitors)
- identify safety issues and/or hazards
- reduce risks or dangers for workers
- support the health and safety consultation and communication
- train and inform workers about health and safety
- provide safe methods of working for each job
- provide the appropriate tools for the job (plant / equipment, safety equipment, protective clothing)
- maintain equipment to reduce risk of injury
- maintain safe entrances and exits
- make available to workers the information about research and relevant materials or substances used in the workplace
Employee’s Responsibilities
- perform work in a safe manner
- observe the safety of other employees and workers
- report health and safety issues / hazards
- assist other employees to follow health and safety policies and law
- use and/or wear protective equipment appropriately
- give reasonable assistance in the case of an accident
Health and Safety Best Practice
Health and Safety best practice documents such as International and Australian / New Zealand standards and approved Codes of Practice which can be industry, occupation, or operational system specific are developed to provide organisations with guidance on implementing best practice requirements. The International Standard for safety is 45001:2018.
There are a wide range of approved safety codes of practice available from the safety authorities.
Safety standards and codes of practice are considered best practice as they are developed by specialist industry and safety bodies. They provide invaluable information on which to build an organisation’s health and safety system.
Guidance Material and Manufacturers / Suppliers Information
Guidance material on specific health and safety topics, developed by and available from the safety authorities and manufacturers or suppliers’ safety documents or manuals provided for safe equipment use and safe chemical use (Safety Data Sheets) also need to be considered and used in building and maintaining a relevant and compliant health and safety system.
Organisation Health and Safety Procedures
Organisation specific health and safety procedures are developed according to the organisations business operations while complying with legislative requirements and considering best practice standards, codes of practice and manufacturers / suppliers documented information.
An organisation’s health and safety procedures along with any accompanying forms, checklists, registers will form the organisations Health and Safety System.